When you want to take your robot wireless but want to take it a step past R/C, an xBee is a prime candidate. The system works over 2.4GHz, similar to WiFi but what it provides is a simple wireless serial bridge. Meaning you can send a packet to the module and it’ll appear at the outputs of all xBees on that network. You don’t have to worry about subnets and IP addresses or any other networking fundamentals, just simple serial communication.

System Design: The Remote
The first step is to design our system. To keep things simple, we’ll have our remote use an Arduino Uno (MCU-050-000) for our microcontroller, an xBee pro (TE-204-AWI) for our radio and a Wireless SD Shield (MCU-064-000) to connect the two together. We’ll also need a joystick to direct the robot. For this project I used our 2-Axis Joystick (TE-128-002).
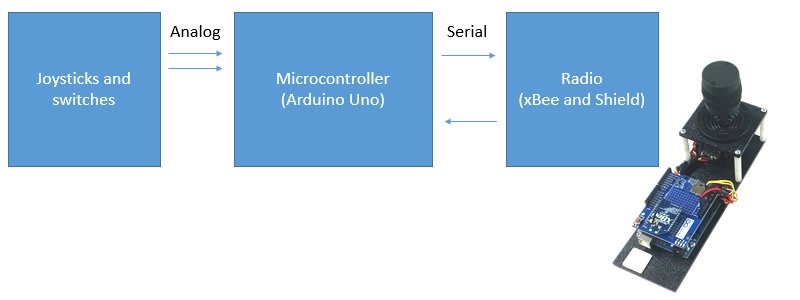
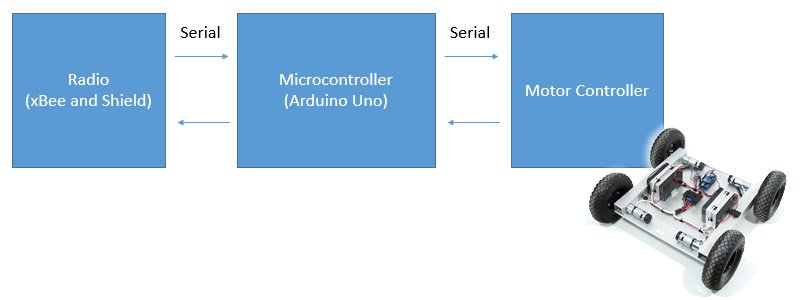
System Design: The Robot
For the robot side, we’ll need the same control scheme, but instead of taking in analogs and sending out data we will be listening to our data stream and sending commands to a motor.
The Code
The majority of the code will largely be a derivative of the Arduino Serial to Serial code from Tech Thursday #005 (Blog Post) (GitHub). However, we’re going to take this a bit further and apply it.
The Code: Remote
/*********************************************************
xBee Remote Example
Author: Jason Traud
SuperDroid Robots
May 7th, 2015
This code uses an Arduino Uno to transmit a basic robot command packet
***********************************************************/
// Analog Input Variables
int FB; // Forward and Back
int LR; // Left and Right
// Temporary variables used in calculations
double tempFB, tempLR, tempSpin;
// Transmitted packet
byte byteFB;
byte byteLR;
byte Digital1;
byte checksum;
// Reverse bits
bool revA0 = 1; // These are used to easily flip
bool revA1 = 0; // the direction of the joystick
// Misc variables
int deadband = 5;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // COM to xBee
}
void loop() {
reinitVars(); // nulls out temporary variables
captureData(); // retrieves new data
packetizeData(); // assembles data to be sent
transmitData(); // send data off to xBee
//debugData(); // print out formatted debug data
delay(20); // Delay needed for consistent communication
}
// Reinitialize temporary variables
void reinitVars() {
Digital1 = 0;
tempFB = 0;
tempLR = 0;
}
// Retrieve analog input data and conform to specs
void captureData() {
FB = analogRead(A0);
LR = analogRead(A1);
// Reverse input analogs if flagged
if (revA0) { FB = 1024 - FB; }
if (revA1) { LR = 1024 - LR; }
// The switch is towards the joystick (full speed)
tempFB = map(FB, 0, 1024, -126, 126);
tempLR = map(LR, 0, 1024, -126, 126);
if ((tempFB > (0 - deadband)) && (tempFB < deadband) )
{ tempFB = 0; }
if ((tempLR > (0 - deadband)) && (tempLR < deadband) )
{ tempLR = 0; }
}
// Assembles data to be sent
void packetizeData() {
// Shift analog data up so we have a range of
// 0-255
tempFB = tempFB + 127;
tempLR = tempLR + 127;
// Assemble the digital packet
// Add status of switches to digital1 here
// convert transmitted data to bytes
byteFB = byte(tempFB);
byteLR = byte(tempLR);
// calculate checksum
checksum = byteFB + byteLR + byte(Digital1);
}
// xBee Communication
void transmitData() {
Serial.write("S");
Serial.write("D");
Serial.write("R");
Serial.write(byteFB);
Serial.write(byteLR);
Serial.write(byte(Digital1));
Serial.write(checksum);
}
// Print out values for easy debugging
void debugData() {
Serial.print("[FB: "); Serial.print(byteFB, HEX); Serial.print("]");
Serial.print("[LR: "); Serial.print(byteLR, HEX); Serial.print("]");
Serial.print("[D1: "); Serial.print(byte(Digital1), BIN); Serial.print("]");
Serial.println("");
}The Code: Robot
/********************************************************* xBee Robot Example Author: Jason Traud SuperDroid Robots May 7th, 2015 This code uses an Arduino Uno mounted on an ATR platform. The robot commands a single Sabertooth motor controller. The goal of this firmware is provide control of the robot over an xBee interface Motor Controller: Sabertooth Dual 25A Motor Driver (TE-091-225) http://www.superdroidrobots.com/shop/item.aspx/sabertooth-dual-25a-motor-driver/822/ ***********************************************************/ #include "Arduino.h" // Arduino // Since the Arduino is limited in the amount of serial COMs it has, // we will control the motor controller over a software Serial port #include#include SoftwareSerial SWSerial(2, 3); // RX on pin 2 (unused), TX on pin 3 (to S1). Sabertooth ST(128, SWSerial); // Address 128, and use SWSerial as the serial port. // Networking related RAM bool sdrFound = false; // Master Flag for SDR bool sFound = false; // Flag for SDR bool dFound = false; // Flag for SDR bool rFound = false; // Flag for SDR // Recieved RAM byte byteFB; byte byteLR; byte Digital1; byte checksum; // Define RAM byte Bad_Tx; word No_Tx = 0; // Used for timeouts unsigned long currentTime; unsigned long timeOfLastGoodPacket = 0; //****************************************************************************** // Sets up our serial com, hardware pins, etc // RETURNS: Nothing //****************************************************************************** void setup() { delay(2000); // Short delay to allow the motor controllers // to power up before we attempt to send it commands. Serial.begin(9600); // xBee SWSerial.begin(9600); // Serial for the motor controller allStop(); // Make sure all motors are stopped for safety } //****************************************************************************** // This is our main program loop and is wrapped in an implied while(true) loop. // RETURNS: Nothing //****************************************************************************** void loop() { currentTime = millis(); processSerial(); // Handle incoming data from xBee timeout(); // Stop the robot if we lost connection delay(10); } //****************************************************************************** // Sets the speed of all motor controllers to zero and sets all ESTOPs // RETURNS: NONE //****************************************************************************** void allStop() { ST.motor(1,0); // Zero motors ST.motor(2,0); } //****************************************************************************** // Here we're trying to find our start bytes. We have a flag for each of the // three bytes (SDR) and we raise the flag as they are found in sequence. If // the next letter is not found, all of the flags are cleared and we start over. // Once we have our flags we wait until we have the expected size of the packet // and then we process the data // RETURNS: NONE //****************************************************************************** void processSerial() { unsigned char inputBufferTemp; byte chksumTest; // Wait for serial if (Serial.available() > 0) { if (!sFound) { inputBufferTemp = Serial.read(); if(inputBufferTemp == 0x53) { sFound = true; } else { sFound = false; dFound = false; rFound = false; sdrFound = false; } } if (!dFound) { inputBufferTemp = Serial.read(); if(inputBufferTemp == 0x44) { dFound = true; } else { sFound = false; dFound = false; rFound = false; sdrFound = false; } } if (!rFound) { inputBufferTemp = Serial.read(); if(inputBufferTemp == 0x52) { rFound = true; sdrFound = true;} else { sFound = false; dFound = false; rFound = false; sdrFound = false; } } if (sdrFound && (Serial.available() > 3 )) { // store bytes into the appropriate variables byteFB = Serial.read(); byteLR = Serial.read(); Digital1 = Serial.read(); checksum = Serial.read(); // Clear flags sdrFound = false; sFound = false; dFound = false; rFound = false; // Calculate our checksum chksumTest = byteFB + byteLR + Digital1; // Compare our calculated checksum to the expected if (chksumTest != checksum) { return; } // We found a good packet, so set current time timeOfLastGoodPacket = currentTime; ST.drive(byteFB); ST.turn(byteLR); } } } //****************************************************************************** // We need to be cautios of data connection losses. Here we are comparing // the current time and when we recieved our last good packet. If a second // has passed then we need to stop our motors // RETURNS: NONE //****************************************************************************** void timeout() { if (currentTime > (timeOfLastGoodPacket + 1000)) { allStop(); timeOfLastGoodPacket = currentTime; } }
Documentation
#techthursday #arduino #xbee #sabertooth




